Garden of Eden

The Garden of Eden (Hebrew: גַּן־עֵדֶן – gan-ʿḖḏen), also called Paradise, is the biblical "garden of God" described in the Book of Genesis and the Book of Ezekiel.[2][3] Genesis 13:10 refers to the "garden of God",[4] and the "trees of the garden" are mentioned in Ezekiel 31.[5][5] The Book of Zechariah and the Book of Psalms also refer to trees and water, without explicitly mentioning Eden.[6]
The name derives from the Akkadian edinnu, from a Sumerian word edin meaning "plain" or "steppe", closely related to an Aramaic root word meaning "fruitful, well-watered".[3] Another interpretation associates the name with a Hebrew word for "pleasure"; thus the Douay-Rheims Bible in Genesis 2:8 has the wording "And the Lord God had planted a paradise of pleasure", rather than "a garden in Eden". The Hebrew term is translated "pleasure" in Sarah's secret saying in Genesis 18:12.[7]
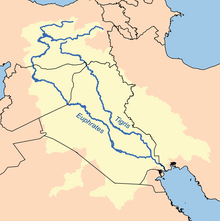
The location of Eden is described in the Book of Genesis as the source of four tributaries. Among scholars who consider it to have been real, there have been various suggestions for its location:[8] at the head of the Persian Gulf, in southern Mesopotamia (now Iraq) where the Tigris and Euphrates rivers run into the sea;[9] and in Armenia.[10][11][12]
Like the Genesis flood narrative, the Genesis creation narrative and the account of the Tower of Babel, the story of Eden echoes the Mesopotamian myth of a king, as a primordial man, who is placed in a divine garden to guard the Tree of Life.[13] The Hebrew Bible depicts Adam and Eve as walking around the Garden of Eden naked, due to their innocence.[14]
The Garden of Eden is considered to be mythological by most scholars.[15][16][17][18]
Biblical narratives[edit]


Genesis[edit]
The second part of the Genesis creation narrative, Genesis 2:4–3:24, opens with YHWH-Elohim (translated here "the LORD God", see Names of God in Judaism) creating the first man (Adam), whom he placed in a garden that he planted "eastward in Eden".[19] "And out of the ground made the Lord God to grow every tree that is pleasant to the sight, and good for food; the tree of life also in the midst of the garden, and the tree of knowledge of good and evil."[20]
The man was free to eat from any tree in the garden except the tree of the knowledge of good and evil. Last of all, the God made a woman (Eve) from a rib of the man to be a companion for the man. In chapter three, the man and the woman were seduced by the serpent into eating the forbidden fruit, and they were expelled from the garden to prevent them from eating of the tree of life, and thus living forever. Cherubim were placed east of the garden, "and a flaming sword which turned every way, to guard the way of the tree of life" (Genesis 3:24).
Genesis 2:10–14 lists four rivers in association with the garden of Eden: Pishon, Gihon, Chidekel (the Tigris), and Phirat (the Euphrates). It also refers to the land of Cush—translated/interpreted as Ethiopia, but thought by some to equate to Cossaea, a Greek name for the land of the Kassites.[21] These lands lie north of Elam, immediately to the east of ancient Babylon, which, unlike Ethiopia, does lie within the region being described.[22] In Antiquities of the Jews, the first-century Jewish historian Josephus identifies the Pishon as what "the Greeks called Ganges" and the Geon (Gehon) as the Nile.[23]
According to Lars-Ivar Ringbom the paradisus terrestris is located in Takab in northeastern Iran.[24]
Ezekiel[edit]
In Ezekiel 28:12–19 the prophet Ezekiel the "son of man" sets down God's word against the king of Tyre: the king was the "seal of perfection", adorned with precious stones from the day of his creation, placed by God in the garden of Eden on the holy mountain as a guardian cherub. But the king sinned through wickedness and violence, and so he was driven out of the garden and thrown to the earth, where now he is consumed by God's fire: "All those who knew you in the nations are appalled at you, you have come to a horrible end and will be no more." (v.19).
According to Terje Stordalen, the Eden in Ezekiel appears to be located in Lebanon.[25] "[I]t appears that the Lebanon is an alternative placement in Phoenician myth (as in Ez 28,13, III.48) of the Garden of Eden",[26] and there are connections between paradise, the garden of Eden and the forests of Lebanon (possibly used symbolically) within prophetic writings.[27] Edward Lipinski and Peter Kyle McCarter have suggested that the Garden of the gods (Sumerian paradise), the oldest Sumerian version of the Garden of Eden, relates to a mountain sanctuary in the Lebanon and Anti-Lebanon ranges.[28]
Proposed locations[edit]

Suggestions for the location of the Garden of Eden include:[8] at its source of the rivers, while others have looked at the head of the Persian Gulf, in southern Mesopotamia (now Iraq) where the Tigris and Euphrates rivers run into the sea;[9] and in the Armenian Highlands or Armenian Plateau.[10][29][11][12] British archaeologist David Rohl locates it in Iran, and in the vicinity of Tabriz, but this suggestion has not caught on with scholarly sources.[30]
The location of Eden is described in the Book of Genesis, chapter 2, verses 10–14:
″And a river departed from Eden to water the garden, and from there it divided and became four tributaries.
The name of the first is Pishon, which is the circumnavigator of the land of Havilah where there is gold. And the gold of this land is good; there are bdellium and cornelian stone. And the name of the second river is Gihon, which is the circumnavigator of the land of Cush.
And the name of the third is Chidekel, which is that which goes to the east of Ashur; and the fourth river is Phirath.″
The Garden of Eden is considered to be mythological by most scholars.[15][16][17][31][18][32]
Parallel concepts[edit]
- Dilmun in the Sumerian story of Enki and Ninhursag is a paradisaical abode[33] of the immortals, where sickness and death were unknown.[34]
- The garden of the Hesperides in Greek mythology was somewhat similar to the Christian concept of the Garden of Eden, and by the 16th century a larger intellectual association was made in the Cranach painting (see illustration at top). In this painting, only the action that takes place there identifies the setting as distinct from the Garden of the Hesperides, with its golden fruit.
- The Persian term "paradise" (borrowed as Hebrew: פרדס, pardes), meaning a royal garden or hunting-park, gradually became a synonym for Eden after c. 500 BCE. The word "pardes" occurs three times in the Hebrew Bible, but always in contexts other than a connection with Eden: in the Song of Solomon iv. 13: "Thy plants are an orchard (pardes) of pomegranates, with pleasant fruits; camphire, with spikenard"; Ecclesiastes 2. 5: "I made me gardens and orchards (pardes), and I planted trees in them of all kind of fruits"; and in Nehemiah ii. 8: "And a letter unto Asaph the keeper of the king's orchard (pardes), that he may give me timber to make beams for the gates of the palace which appertained to the house, and for the wall of the city." In these examples pardes clearly means "orchard" or "park", but in the apocalyptic literature and in the Talmud "paradise" gains its associations with the Garden of Eden and its heavenly prototype, and in the New Testament "paradise" becomes the realm of the blessed (as opposed to the realm of the cursed) among those who have already died, with literary Hellenistic influences.
Other views[edit]
Jewish eschatology[edit]
In the Talmud and the Jewish Kabbalah,[35] the scholars agree that there are two types of spiritual places called "Garden in Eden". The first is rather terrestrial, of abundant fertility and luxuriant vegetation, known as the "lower Gan Eden". The second is envisioned as being celestial, the habitation of righteous, Jewish and non-Jewish, immortal souls, known as the "higher Gan Eden". The rabbis differentiate between Gan and Eden. Adam is said to have dwelt only in the Gan, whereas Eden is said never to be witnessed by any mortal eye.[35]
According to Jewish eschatology,[36][37] the higher Gan Eden is called the "Garden of Righteousness". It has been created since the beginning of the world, and will appear gloriously at the end of time. The righteous dwelling there will enjoy the sight of the heavenly chayot carrying the throne of God. Each of the righteous will walk with God, who will lead them in a dance. Its Jewish and non-Jewish inhabitants are "clothed with garments of light and eternal life, and eat of the tree of life" (Enoch 58,3) near to God and His anointed ones.[37] This Jewish rabbinical concept of a higher Gan Eden is opposed by the Hebrew terms gehinnom[38] and sheol, figurative names for the place of spiritual purification for the wicked dead in Judaism, a place envisioned as being at the greatest possible distance from heaven.[39]
In modern Jewish eschatology it is believed that history will complete itself and the ultimate destination will be when all mankind returns to the Garden of Eden.[40]
Legends[edit]
In the 1909 book Legends of the Jews, Louis Ginzberg compiled Jewish legends found in rabbinic literature. Among the legends are ones about the two Gardens of Eden. Beyond Paradise is the higher Gan Eden, where God is enthroned and explains the Torah to its inhabitants. The higher Gan Eden contains three hundred ten worlds and is divided into seven compartments. The compartments are not described, though it is implied that each compartment is greater than the previous one and is joined based on one's merit. The first compartment is for Jewish martyrs, the second for those who drowned, the third for "Rabbi Johanan ben Zakkai and his disciples," the fourth for those whom the cloud of glory carried off, the fifth for penitents, the sixth for youths who have never sinned; and the seventh for the poor who lived decently and studied the Torah.[41]
In chapter two, Legends of the Jews gives a brief description of the lower Gan Eden. The tree of knowledge is a hedge around the tree of life, and it is so vast that it would take one over five hundred years to clear a path through the tree of knowledge to reach the tree of life. From beneath the trees flow all the world's waters in the form of four rivers: Tigris, Nile, Euphrates, and Ganges. After the fall of man, the world was no longer irrigated by this water. While in the garden, though, Adam and Eve were served meat dishes by angels and the animals of the world understood human language, respected mankind as God's image, and feared Adam and Eve. When one dies, one's soul must pass through the lower Gan Eden in order to reach the higher Gan Eden. The way to the garden is the Cave of Machpelah that Adam guards. The cave leads to the gate of the garden, guarded by a cherub with a flaming sword. If a soul is unworthy of entering, the sword annihilates it. Within the garden is a pillar of fire and smoke that extends to the higher Gan Eden, which the soul must climb in order to reach the higher Gan Eden.[41]
Islamic view[edit]

The term jannāt ʿadni ("Gardens of Eden" or "Gardens of Perpetual Residence") is used in the Qur'an for the destination of the righteous. There are several mentions of "the Garden" in the Qur'an (2:35, 7:19, 20:117, 61:12), while the Garden of Eden, without the word ʿadn,[42] is commonly the fourth layer of the Islamic heaven and not necessarily thought as the dwelling place of Adam.[43] The Quran refers frequently over various Surah about the first abode of Adam and Hawwa (Eve), including surat Sad, which features 18 verses on the subject (38:71–88), surat al-Baqara, surat al-A'raf, and surat al-Hijr although sometimes without mentioning the location. The narrative mainly surrounds the resulting expulsion of Hawwa and Adam after they were tempted by Shaitan. Despite the Biblical account, the Quran mentions only one tree in Eden, the tree of immortality, which God specifically claimed it was forbidden to Adam and Eve. Some exegesis added an account, about Satan, disguised as a serpent to enter the Garden, repeatedly told Adam to eat from the tree, and eventually both Adam and Eve did so, resulting in disobeying God.[44] These stories are also featured in the hadith collections, including al-Tabari.[45]
Latter Day Saints[edit]
Followers of the Latter Day Saints movement (also known as Mormons) believe that after Adam and Eve were expelled from the Garden of Eden they resided in a place known as Adam-ondi-Ahman, located in present-day Daviess County, Missouri. It is recorded in the Doctrine and Covenants that Adam blessed his posterity there and that he will return to that place at the time of the final judgement[46][47] in fulfillment of a prophecy set forth in the Book of Mormon.[48]
Numerous early leaders of the Church, including Brigham Young, Heber C. Kimball, and George Q. Cannon, taught that the Garden of Eden itself was located in nearby Jackson County, Missouri,[49] but there are no surviving first-hand accounts of that doctrine being taught by Joseph Smith himself. LDS doctrine is unclear as to the exact location of the Garden of Eden, but tradition among Latter-Day Saints places it somewhere in the vicinity of Adam-ondi-Ahman, or in Jackson County.[50][51]
Art[edit]
The Garden of Eden motifs most frequently portrayed in illuminated manuscripts and paintings are the "Sleep of Adam" ("Creation of Eve"), the "Temptation of Eve" by the Serpent, the "Fall of Man" where Adam takes the fruit, and the "Expulsion". The idyll of "Naming Day in Eden" was less often depicted. Much of Milton's Paradise Lost occurs in the Garden of Eden. Michelangelo depicted a scene at the Garden of Eden in the Sistine Chapel ceiling. In the Divine Comedy, Dante places the Garden at the top of Mt. Purgatory. For many medieval writers, the image of the Garden of Eden also creates a location for human love and sexuality, often associated with the classic and medieval trope of the locus amoenus.[52] One of oldest depictions of Garden of Eden is made in Byzantine style in Ravenna, while the city was still under Byzantine control. A preserved blue mosaic is part of the mausoleum of Galla Placidia. Circular motifs represent flowers of the garden of Eden.
The Garden of Eden by Lucas Cranach der Ältere, a 16th-century German depiction of Eden
The Garden of Eden with the Fall of Man by Jan Brueghel the Elder and Pieter Paul Rubens, c. 1615, depicting both domestic and exotic wild animals such as tigers, parrots and ostriches co-existing in the garden
Fifth century "Garden of Eden" mosaic in mausoleum of Galla Placidia in Ravenna, Italy. UNESCO World Heritage Site.
The Garden of Eden by Thomas Cole (c. 1828)
After wandering through the Garden of Eden, Eve takes the forbidden fruit while Lilith speaks to Adam (by Carl Poellath, c. 1886)
The Garden of Eden by Adi Holzer (2012)
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ Gibson, Walter S. Hieronymus Bosch. New York:Hudson, 1973. p. 26. ISBN 0-500-20134-X
- ^ Metzger, Bruce Manning; Coogan, Michael D (2004). The Oxford Guide To People And Places Of The Bible. Oxford University Press. p. 62. ISBN 978-0-19-517610-0. Retrieved 22 December 2012.
- ^ a b Cohen 2011, pp. 228–229
- ^ "oremus Bible Browser : Genesis 13". bible.oremus.org. Retrieved 2018-10-31.
- ^ a b "oremus Bible Browser : Ezekiel 31". bible.oremus.org. Retrieved 2018-10-31.
- ^ Tigchelaar 1999, p. 37
- ^ H5731 Eden – The same as H5730 (masculine); Eden= "pleasure" ... the first habitat of man after the creation; site unknown
- ^ a b Wilensky-Lanford, Brook (2012). Paradise Lust: Searching for the Garden of Eden. Grove Press.
paradise lust.
- ^ a b Hamblin, Dora Jane (May 1987). "Has the Garden of Eden been located at last? (Dead Link)" (PDF). Smithsonian. 18 (2). Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 January 2014. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
- ^ a b Zevit, Ziony. What Really Happened in the Garden of Eden? 2013. Yale University Press, p. 111.
- ^ a b Duncan, Joseph E. Milton's Earthly Paradise: A Historical Study of Eden. 1972. University Of Minnesota Press, pp. 96, 212.
- ^ a b Scafi, Alessandro. Return to the Sources: Paradise in Armenia, in: Mapping Paradise: A History of Heaven on Earth. 2006. London-Chicago: British Library-University of Chicago Press, pp. 317–322
- ^ Davidson 1973, p. 33.
- ^ Donald Miller (2007) Miller 3-in-1: Blue Like Jazz, Through Painted Deserts, Searching for God, Thomas Nelson Inc, ISBN 978-1418551179, p. PT207
- ^ a b Levenson 2004, p. 11 "How much history lies behind the story of Genesis? Because the action of the primeval story is not represented as taking place on the plane of ordinary human history and has so many affinities with ancient mythology, it is very far-fetched to speak of its narratives as historical at all."
- ^ a b Schwartz, Howard; Loebel-Fried, Caren; Ginsburg, Elliot K. (2007). Tree of Souls: The Mythology of Judaism. Oxford University Press. p. 704.
- ^ a b George, Arthur; George, Elena (2014). The Mythology of Eden. Hamilton Books. p. 458.
- ^ a b Graves, Robert; Patai, Raphael (1986). Hebrew Myths: The Book of Genesis. Random House. p. 315.
- ^ Levenson 2004, p. 13 "The root of Eden denotes fertility. Where the wondrously fertile gard was thought to have been located (if a realistic location was ever conceived) is unclear. The Tigris and Euphrates are the two great rivers of the Mesopotamia (now found in modern Iraq). But the Piston is unidentified, and the only Gihon in the Bible is a spring in Jerusalem (1 Kings 1.33, 38)."
- ^ Genesis 2:9
- ^ "The Jewish Quarterly Review". The Jewish Quarterly Review. University of Pennsylvania Press. 64–65: 132. 1973. ISSN 1553-0604. Retrieved 2014-02-19.
...as Cossaea, the country of the Kassites in Mesopotamia [...]
- ^ Speiser 1994, p. 38
- ^ Josephus, Antiquities of the Jews. Book I, Chapter 1, Section 3.
- ^ Lars-Ivar Ringbom, Paradisus Terrestris. Myt, Bild Och Verklighet, Helsingfors, 1958.
- ^ Stordalen 2000, p. 164
- ^ Brown 2001, p. 138
- ^ Swarup 2006, p. 185
- ^ Smith 2009, p. 61
- ^ Day, John. Yahweh and the Gods and Goddesses of Canaan. 2002. Sheffield Academic Press, p. 30.
- ^ Cline, Eric H. (2007). From Eden to Exile: Unraveling Mysteries of the Bible. National Geographic. p. 10. ISBN 978-1-4262-0084-7.
- ^ Delumeau, Jean; O'Connell, Matthew (2000). History of Paradise: The Garden of Eden in Myth and Tradition. University of Illinois Press. p. 276.
- ^ Albright, W. F. (October 1922). "The Location of the Garden of Eden". The American Journal of Semitic Languages and Literatures. The University of Chicago Press. 39 (1): 15–31. doi:10.1086/369964. JSTOR 528684.
- ^ Mathews 1996, p. 96.
- ^ Cohen 2011, p. 229.
- ^ a b Gan Eden – JewishEncyclopedia; 02-22-2010.
- ^ Olam Ha-Ba – The Afterlife - JewFAQ.org; 02-22-2010.
- ^ a b Eshatology – JewishEncyclopedia; 02-22-2010.
- ^ "Gehinnom is the Hebrew name; Gehenna is Yiddish." Gehinnom – Judaism 101 websourced 02-10-2010.
- ^ "Gan Eden and Gehinnom". Jewfaq.org. Retrieved 2011-06-30.
- ^ "End of Days". End of Days. Aish. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
- ^ a b The Sacred Texts: Legends of the Jews, Chapter 1
- ^ See list of occurrences.
- ^ Patrick Hughes, Thomas Patrick Hughes Dictionary of Islam Asian Educational Services 1995 ISBN 978-8-120-60672-2 p. 133
- ^ Leaman, Oliver The Quran, an encyclopedia, p. 11, 2006
- ^ Wheeler, Brannon Mecca and Eden: ritual, relics, and territory in Islam p. 16, 2006
- ^ "Doctrine and Covenants 107:53".
- ^ "Doctrine and Covenants 116:1".
- ^ "Daniel 7:13–14, 22".
- ^ "Joseph Smith/Garden of Eden in Missouri", FairMormon Answers
- ^ Bruce A. Van Orden, "I Have a Question: What do we know about the location of the Garden of Eden?", Ensign, January 1994, pp. 54–55.
- ^ "What is Mormonism? Overview of Mormon Beliefs – Mormonism 101". www.mormonnewsroom.org. 2014-10-13. Archived from the original on 2012-03-10. Retrieved 2018-10-31.
- ^ Curtius 1953, p. 200, n.31
Bibliography[edit]
- Brown, John Pairman (2001). Israel and Hellas, Volume 3. Walter de Gruyter. ISBN 9783110168822.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Cohen, Chaim (2011). "Eden". In Berlin, Adele; Grossman, Maxine (eds.). The Oxford Dictionary of the Jewish Religion. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780199730049.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Curtius, Ernst Robert (1953). European Literature and the Latin Middle Ages. Princeton UP. ISBN 978-0-691-01899-7.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link) Translated by Willard R. Trask.
- Davidson, Robert (1973). Genesis 1-11 (commentary by Davidson, R. 1987 [Reprint] ed.). Cambridge, Eng.: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521097604.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Levenson, Jon D. (2004). "Genesis: Introduction and Annotations". In Berlin, Adele; Brettler, Marc Zvi (eds.). The Jewish Study Bible. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780195297515.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Mathews, Kenneth A. (1996). Genesis. Nashville, Tenn.: Broadman & Holman Publishers. ISBN 9780805401011.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Smith, Mark S. (2009). "Introduction". In Pitard, Wayne T. (ed.). The Ugaritic Baal Cycle, volume II. BRILL. ISBN 9004153489.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Speiser, E.A. (1994). "The Rivers of Paradise". In Tsumura, D.T.; Hess, R.S. (eds.). I Studied Inscriptions from Before the Flood. Eisenbrauns. ISBN 9780931464881.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Stordalen, Terje (2000). Echoes of Eden. Peeters. ISBN 9789042908543.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Swarup, Paul (2006). The self-understanding of the Dead Sea Scrolls Community. Continuum.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Tigchelaar, Eibert J. C. (1999). "Eden and Paradise: The Garden Motif in some Early Jewish Texts (1 Enoch and Other Texts Found at Qumran)". In Luttikhuizen, Gerard P (ed.). Paradise Interpreted. Themes in Biblical narrative. Leiden: Konninklijke Brill. ISBN 90 04 11331 2.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Willcocks, Sir William, Hormuzd Rassam. Mesopotamian Trade. Noah's Flood: The Garden of Eden, in: The Geographical Journal 35[permanent dead link], No. 4 (April 1910). DOI: 10.2307/1777041[dead link]
External links[edit]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Garden of Eden. |
| Look up Garden of Eden in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |