Buskin
This article needs additional citations for verification. (November 2006) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to cothurns. |
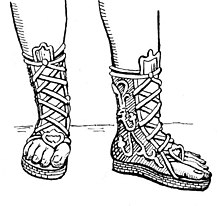
A buskin is a knee- or calf-length boot made of leather or cloth which laces closed, but is open across the toes. A high-heeled version was worn by Athenian tragic actors (to make them look taller). It was also worn by hunters, and soldiers in Ancient Greek, Etruscan, and Roman societies, to protect the lower legs against thorns, dirt, etc.
The word buskin, only recorded in English since 1503 meaning "half boot", is of unknown origin, perhaps from Old French brousequin (in modern French brodequin) or directly from its Middle Dutch model brosekin "small leather boot". Figurative senses relating to tragedy are from the word being used (since 1570) to translate Greek kothornos (Greek: κόθορνος) or Latin cothurnus, the high, thick-soled boot worn in Athenian tragedy; contrasted with sock (from Latin soccus), the low shoe worn by comedians.
Byzantine emperors were formally clad in purple buskins, embroidered in gold with double-headed eagles.[1]
Roman Catholic Church[edit]
In the Roman Catholic Church, buskins are ceremonial liturgical stockings (caligae in Latin) of silk, sometimes interwoven with gold threads and even heavily embroidered, formerly worn by the celebrant of a pontifical Mass.[2] The buskins can be worn over the episcopal sandals, regular dress socks with regular dress shoes, or over the red papal shoes worn by the Pope.
Originally liturgical buskins were worn by all priests, until about the eighth century when they were reserved for the exclusive use of bishops as part of the pontificalia, i.e. episcopal "regalia", a privilege in modern times extended to some lesser prelates. In liturgical colour they correspond to the chasuble, but are never worn with black.
References[edit]
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Buskin. |
- ^ John Julius Norwich, A Short History of Byzantium, Penguin 1998, p. 248.
- ^ "Buskin". Catholic Encyclopedia.
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Herbermann, Charles, ed. (1913). "Buskins". Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Herbermann, Charles, ed. (1913). "Buskins". Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company.